目录
对 map 的使用方法和底层机制进行记录,以下内容基于 go1.22.1 版本。
Go 中的 map 就是哈希表,比较类似的就是 python 的dict。
1 使用方法
增删改查示例代码:
gotestMap := make(map[string]string, 10) // 初始化
testMap["test1"] = "test1" // 增
testMap["test1"] = "test2" // 改
delete(testMap, "test1") // 删 删除的键不存在也不会报错
if value, ok := testMap["test1"]; ok { // 查
fmt.Println(value)
}
有几个注意点:
- 向一个没有 make 初始化过的,实质为 nil 的 map 写入数据会引发 panic,但是查找和删除并不会引发 panic,访问其长度会返回0。
- 即使 map 中没有对应的键,delete 也不会报错,查询也会返回对应类型的零值。
- make 一个新的 map 时,可以顺带指定其容量,当然不指定也行,但是在有数据预期的情况下,指定容量会减少 map 扩容的次数,加快速度。
- 查数据的时候,建议带上 ok,方便很多。
- map 并不支持并发读写,如果底层检测到了读写冲突,会直接引发 panic。
2 底层实现
偷一张现成的图
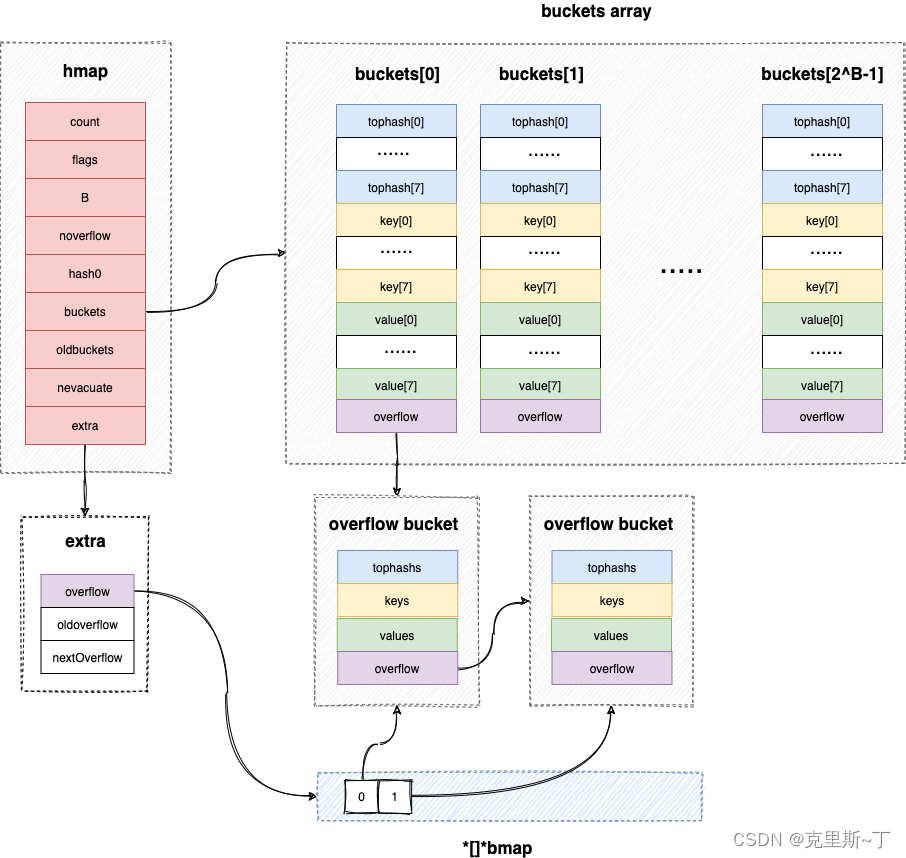
map 相关的底层数据结构如下:
go// src/runtime/map.go
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/reflectdata/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
// map 保存的键值对数量
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
// bucket 数组长度为2的 B 次方
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
// 当前使用的 bucket 数组
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
// 扩容后的旧的等待数组迁移的 bucket 数组
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
// mapextra holds fields that are not present on all maps.
type mapextra struct {
// If both key and elem do not contain pointers and are inline, then we mark bucket
// type as containing no pointers. This avoids scanning such maps.
// However, bmap.overflow is a pointer. In order to keep overflow buckets
// alive, we store pointers to all overflow buckets in hmap.extra.overflow and hmap.extra.oldoverflow.
// overflow and oldoverflow are only used if key and elem do not contain pointers.
// overflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.buckets.
// oldoverflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.oldbuckets.
// The indirection allows to store a pointer to the slice in hiter.
// 如果键值都不是指针 那么这个 map 会被标记为没有指针 以避免 gc 扫描整个 map
// 但是 bmap.overflow 是一个指针
// 为了保证其存活 将所有的 overflow 指向的 bucket 全部存储到 hmap.extra.overflow 和 hmap.extra.oldoverflow
// 这间接地允许在 hiter 里存储指向切片的指针
// 注 hiter 是针对 map 的迭代器 不是这里的讨论重点
overflow *[]*bmap
oldoverflow *[]*bmap
// nextOverflow holds a pointer to a free overflow bucket.
nextOverflow *bmap
}
go// src/cmd/compile/reflectdata/reflect.go
// Builds a type representing a Bucket structure for
// the given map type. This type is not visible to users -
// we include only enough information to generate a correct GC
// program for it.
// Make sure this stays in sync with runtime/map.go.
//
// 该类型对用户不可见 只确保在 gc 里面正确即可
//
// A "bucket" is a "struct" {
// tophash [BUCKETSIZE]uint8 // bucket 存储的键的 hash 值的高8位
// keys [BUCKETSIZE]keyType // 键
// elems [BUCKETSIZE]elemType // 值
// overflow *bucket // 指向下一个 bucket 的指针
// }
// src/runtime/map.go
// A bucket for a Go map.
// 这个就是 bucket 的对用户可见的版本
type bmap struct {
// tophash generally contains the top byte of the hash value
// for each key in this bucket. If tophash[0] < minTopHash,
// tophash[0] is a bucket evacuation state instead.
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
// Followed by bucketCnt keys and then bucketCnt elems.
// NOTE: packing all the keys together and then all the elems together makes the
// code a bit more complicated than alternating key/elem/key/elem/... but it allows
// us to eliminate padding which would be needed for, e.g., map[int64]int8.
// Followed by an overflow pointer.
// 这段注释解释了为什么 bucket 里面键和值是分开存储的
// 注释说 虽然这样会加重代码复杂性 但是利于消除间隔
// 我认为 这个 “消除间隔”(eliminate padding)指的是内存对齐
}
后两个成员变量实质上并不存在,在访问时是通过指针偏移来访问。
- 总结一下,map 的底层结构是这样的:hmap 用数组存储一系列 bucket,每个 bucket 代表着一种 hash 匹配结果,并且存储着 hash 低位值相同的键值对(实质上就是发生了哈希冲突的键值对)。当一个 bucket 存储的冲突的键值对太多,一个bucket存储不过来,那么会创建一个新的 bucket,老的 bucket 的 overflow 指向新的 bucket,形成一个 bucket 链表结构。
- 引入一个新的概念:负载因子,它通过计算 map 存储的键值对数量和底层的 bucket 数量得到。如果负载因子过大,说明哈希冲突严重;如果负载因子过小,说明键值对过于分散,没有有效利用内存。而后者这个情况一般会出现在 map 被大量删除键值对后出现。
负载因子这个概念,在采用了相同方法实现的哈希表中是通用的,比如 redis。
-
当负载因子超过6.5时,说明平均一个 bucket 里面存储了超过6.5个键值对,会触发 rehash,包括对 bucket 数组进行扩容,申请更多的 bucket 并且重新组织所有的键值对。
-
除了负载因子过高这种情况外,如果通过 overflow 组织的 bucket 数量达到时,也会触发 bucket 数组的扩容。因为这种情况说明哈希冲突非常严重,bucket 链表长度过长,可能影响读写效率。
-
扩容分为两种:增量扩容和等量扩容。
- 增量扩容是这样的:oldbuckets 指针指向即将要替换的那个老 bucket 数组,创建一个长度等于老 bucket 数组的两倍的新 bucket 数组。如果 map 存储的数据量极其大,那么这次扩容并不会将所有 bucket 全部写入新的数组,而是在每次读写的时候向新的数组写入两个 bucket,直到旧的数组的 bucket 的数据全部搬到新的数组里面之后 释放旧数组的内存空间。
- 等量扩容是为了应对负载因子过低这种情况的,它会重新组织 bucket,回收没有用到的 bucket,加快查询速度。
注意,如果旧数组内还有 bucket,查询的时候都会优先进旧的 bucket 进行查询。
- 对于增删改查来说,本质都是根据键值找到正确的 bucket 和对应的 value。第一步是计算键值的哈希值,得到的哈希值的低位与
hmap.B取模得到 bucket 在 buckets 数组内的位置,哈希值的高位用于在 bucket 内的 tophash 数组查找对应的下标(一个 bucket 找不到的话会继续沿着 bucket 链表继续找下去)。
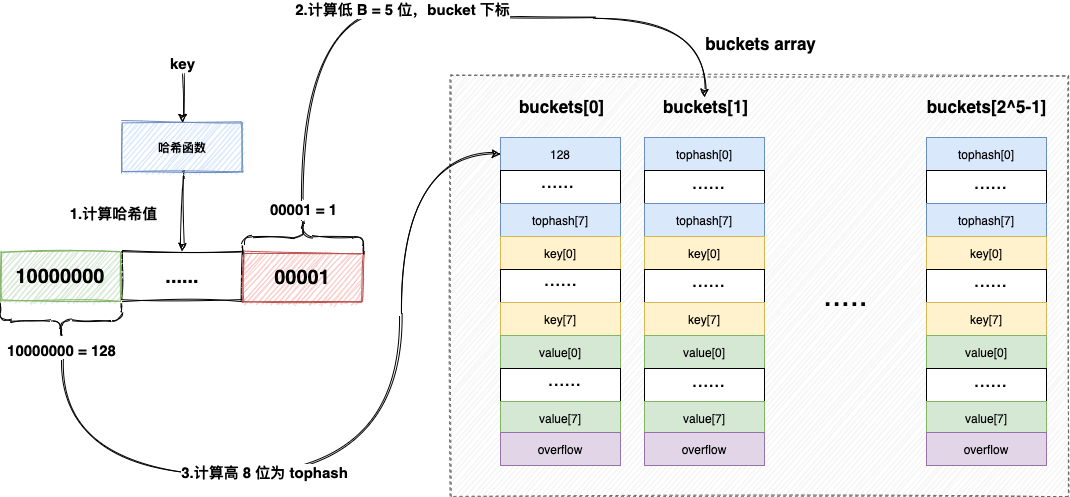
- 注意,如果 map 处于 bucket 搬迁的过程中,添加/更新键值对也会和查询一样,从旧的 bucket 数组开始查,但是最终如果是添加而不是更新键值对的话,添加一定是添加到新的 bucket 数组中。
- 以上的内容都没有提到的是 hmap 的 extra 字段。它是一个可选字段,当 map 的键值对全部不是指针类型时启用,以避免触发 gc 时扫描整个 map 降低 gc 的速度。这些在注释中都说了,但是有一点没有说全:如何解决
bmap.overflow是个指针?
go// src/cmd/compile/reflectdata/reflect.go
// MapBucketType 为 map 创建一个给定类型的 bucket
// MapBucketType makes the map bucket type given the type of the map.
func MapBucketType(t *types.Type) *types.Type {
if t.MapType().Bucket != nil { // 复用
return t.MapType().Bucket
}
...
// If keys and elems have no pointers, the map implementation
// can keep a list of overflow pointers on the side so that
// buckets can be marked as having no pointers.
// Arrange for the bucket to have no pointers by changing
// the type of the overflow field to uintptr in this case.
// See comment on hmap.overflow in runtime/map.go.
otyp := types.Types[types.TUNSAFEPTR]
if !elemtype.HasPointers() && !keytype.HasPointers() {
otyp = types.Types[types.TUINTPTR]
}
overflow := makefield("overflow", otyp)
field = append(field, overflow)
...
return bucket
}
看注释,在 map 的键值都不是指针的情况下,hmap.overflow就是 uintptr 类型(一个数值类型而不是指针类型)而不是指针类型。
关于 gc(垃圾回收)机制,以后会写。
* 参考链接
本文作者:御坂19327号
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录